Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (44): 7797-7802.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.44.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Intensive care after transplantation
Suo You-jun, Xu Hong-shan, Gong Li
- Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2013-10-29Published:2013-10-31 -
Contact:Xu Hong-shan, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China 3199800901@163.com -
About author:Suo You-jun★, Master, Attending physician, Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China suoyoujun@hotmail.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Suo You-jun, Xu Hong-shan, Gong Li. Intensive care after transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(44): 7797-7802.
share this article
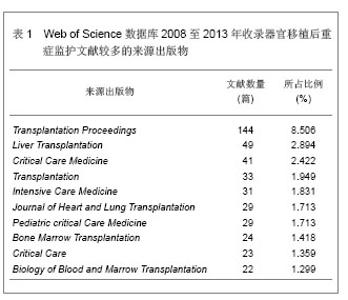
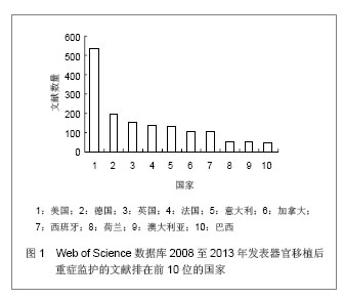
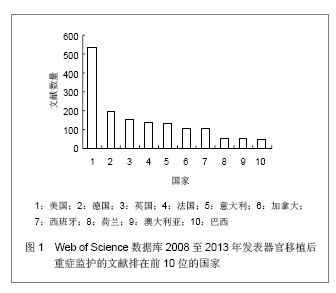
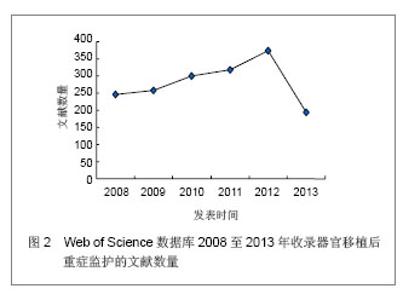
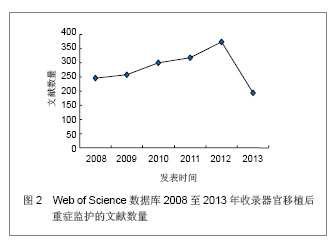
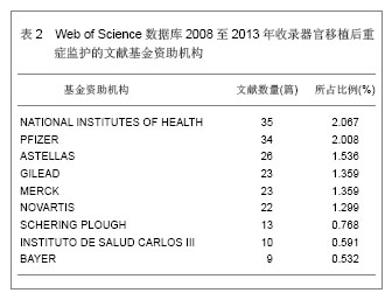
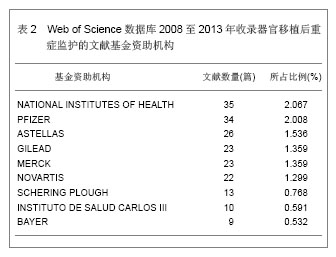
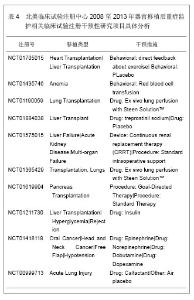
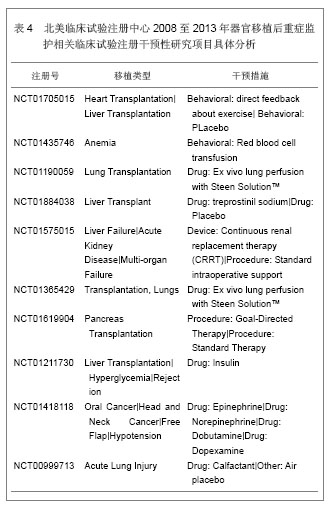
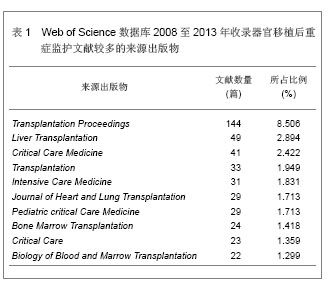
Web of Science数据库2008至2013年收录器官移植后重症监护的1 693篇文献中,美国发表文献最多,532篇,占文献总数的31.424%,其次为德国,196篇,英国152篇,法国140篇,意大利132篇,加拿大107篇,西班牙105篇,其他国家文献数量不足100篇。Web of Science数据库2008至2013年收录器官移植后重症监护的文献前10位的国家没有亚洲国家,说明亚洲国家在器官移植后重症监护研究领域不具优势。 2.1.2 文献类型 Web of Science数据库收录2008至2013年收录器官移植后的重症监护相关文献以研究原著为主,其中研究原著1 338篇,占文献总数的79.031%,综述259篇,占15.298%,会议文章171篇,会议摘要47篇,文章章节41篇,编辑材料2篇,快报1篇。研究原著的篇数远远多于其他类型的文献。 2.1.3 机构分布 Web of Science数据库2008至2013年收录器官移植后重症监护的文献数量排在前10位的机构有美国匹兹堡大学(University of Pittsburgh)发表文献34篇,加拿大多伦多大学(University of Toronto)发表文献30篇,加拿大阿尔伯塔大学(University of Alberta)发表文献28篇,德国汉诺威医学院(Hannover Medical School)发表文献26篇,美国梅奥医学中心(Mayo Clinic)发表文献25篇,美国哈佛大学(Harvard University)发表文献24篇,其他机构发表文献数量较少。 2.1.4 来源期刊 Web of Science数据库2008至2013年收录器官移植后重症监护的文献以重症和移植医学类杂志较多,Transplantation Proceedings (《移植学会会刊》)发表文献最多,144篇,占全部文献的8.506%,Liver Transplantation (《肝移植》)发表文献量49篇,Critical Care Medicine (《新地平线》)发表文献41篇,Transplantation发表文献33篇,Intensive Care Medicine(《重症监护医学》)发表文献31篇,其他杂志发表文献数量不足30篇。通过来源期刊的统计分析,可帮助器官移植后重症监护研究者及时了解和掌握器官移植后重症监护的核心出版物,确定跟踪研究的文献基础,同时可以用于指导投稿,指导研究者尽可能选择学科类别与收录相关文献量大、收录侧重与研究内容相一致的期刊,提高文献命中率,有利于在器官移植后重症监护领域扩大研究成果的影响范围。Web of Science数据库2008至2013年收录器官移植后重症监护的文献较多的来源出版物,见表1。"
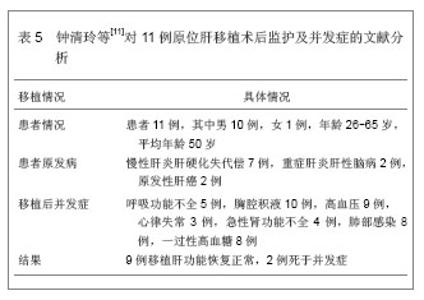
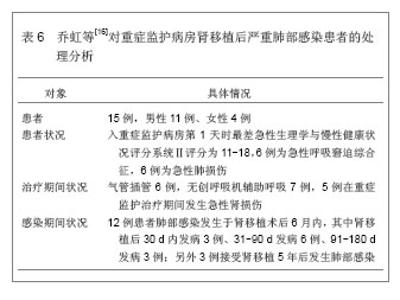
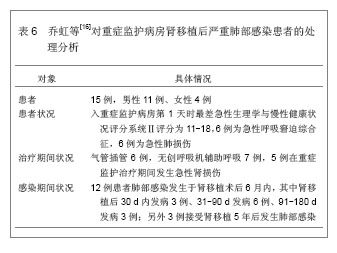
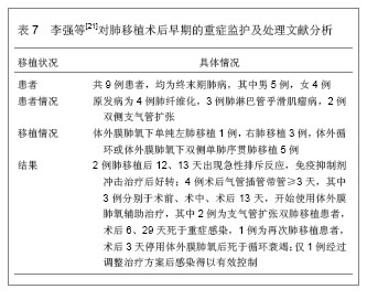
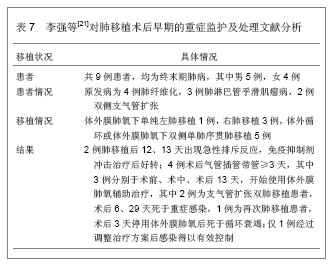
| [1]Al-Qadheeb NS, Hoffmeister J, Roberts R, et al. Perceptions of Nurses and physicians of their communication at night about intensive care patients' pain, agitation, and delirium. Am J Crit Care. 2013;22(5):e49-e61. [2]Jurado LV, Steelman JD. The role of the pharmacist in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2013;36(4):407-414. [3]王祥飞.重症监护室护理管理[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2009,8(5):134-135. [4]Liu W, Tan J, Sun J, et al. Invasive candidiasis in intensive care units in China: in vitro antifungal susceptibility in the China-SCAN study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. [5]Darbyshire JL, Young JD. An investigation of sound levels on intensive care units with reference to the WHO guidelines. Crit Care. 2013;17(5):R187. [6]陈规划,蔡常洁.肝移植围手术期的管理[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2002,23(6):325-326. [7]Lewis MB, Howdle PD. Neurologic complications of liver transplantation in adults. Neurology. 2003;61(9):1174-1178. [8]Yu J, Zheng SS, Liang TB, et al. Possible causes of central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(17):2540-2543. [9]蔡常洁,陈规划,管向东,等.肝移植术后细菌性感染的病原学特征及分布特点[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(15):1026-1028. [10]席淑华,张群,吕一刚,等.肝移植重症监护室医院感染的前瞻性研究[J].解放军护理杂志,2009,26(9):36-37. [11]钟清玲,胡庆霞,薛广燕.11例原位肝移植术后监护及并发症分 析[J].实用临床医学,2005,6(12):177-179. [12]Horn DL, Neofytos D, Anaissie EJ, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of candidemia in 2019 patients: data from the prospective antifungal therapy alliance registry. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(12):1695-1703. [13]黄樱,王红.肾移植术后的肺部感染特点[J].中国临床康复,2006, 10(45):172-173. [14]Randhawa PS, Schonder K, Shapiro R, et al. Polyomavirus BK neutralizing activity in human immunoglobulin preparations. Transplantation. 2010;89(12):1462-1465. [15]秦国初,周正扬,颐康康,等.肾移植后巨细胞病毒肺炎的影像学诊断[J].临床放射学杂志,2006,25(7):619-621. [16]乔虹,王东信,李双玲,等.外科重症监护病房肾移植术后严重肺部感染患者的处理[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2011,20(5):406-411. [17]Chen F, Chin K, Sato M, et al. Postoperative respiratory management in living donor lobar lung transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2013;27(4):E383-390. [18]宫玉翠,阮亮.建立肺移植术后ICU监护专业小组的探索[J].中国护理管理,2010,10(3):35-36. [19]Zhao KJ, Wu XQ, Chen JY, et al. Early cardiovascular complications post lung transplantation. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2013;41(4):310-314. [20]Masnou N, Rello J. The impact of lung transplantation on ICU personnel. Med Intensiva. 2013;37(3):206-208. [21]李强,马旭晨,卢家凯,等.肺移植术后早期的重症监护及处理[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2012,28(8):473-475. [22]Pappas PG, Kauffman CA, Andes D, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of candidiasis: 2009 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(5):503-535. [23]敖俊红,杨燕妮,钟白玉,等.重症监护及移植病房环境真菌监测研究[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2007,17(9):1103-1106. |
| [1] | Xuan Juanjuan, Bai Hongtai, Zhang Jixiang, Wang Yaoquan, Chen Guoyong, Wei Sidong. Role of regulatory T cell subsets in liver transplantation and progress in clinical application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1143-1148. |
| [2] | Yang Zhiwei, Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao. Relationship between tacrolimus metabolic rate and early BK virus infection after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 712-716. |
| [3] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [4] | Wang Xiaobo, Wang Changan, Han Jianle, Yang Qingyan, Yang Shuaiping, Yang Junwei. Influence of conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus on glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk profiles in stable kidney transplant patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2236-2240. |
| [5] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [6] | Liu Junchang, Gao Xiaolin, Jiang Taimao. Correlation of CY3A5 genetic polymorphism with concentration/dosage of tacrolimus and individualized administration of tacrolimus after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1740-1744. |
| [7] | Guo Juan, Zheng Shan, Xie Hui, Hu Yahui. An analysis of pathogenic bacteria infection in 422 kidney transplant recipients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5198-5202. |
| [8] | Liu Luhao, Fang Jiali, Zhang Lei, Li Guanghui, Xu Lu, Lai Xingqiang, Xiong Yunyi, Chen Rongxin, Ma Junjie, Chen Zheng. Clinical assessment criteria of donor pancreas transplants for simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4157-4161. |
| [9] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [10] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [11] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [12] | Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2625-2629. |
| [13] | Yang Jin, Zhang Meixia, Yan Pei, Cheng Qiao, Li Jianzhen . Meta-analysis of risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2450-2460. |
| [14] | Jiang Shanshan, Wang Feng, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells and their application in organ transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 103-109. |
| [15] | Yang Qi-shun1, Jiang Wei1, Huang Chi-bing2. Staging diagnosis and treatment for pulmonary infection after renal transplantation can improve the stability of transplanted renal functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(8): 1255-1260. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||